Git Rebase
What is Git Rebase? - Conceptual Overview
When I first encountered the git rebase command, I found it confusing. Like many git commands, it can be unwieldy and the user experience is not always intuitive. However, the purpose of rebase is simple: to integrate changes from one branch into another, much like the merge command.
The key difference between rebase and merge lies in their approach to achieving this integration. To understand this difference, lets first examine how git merge works.
git merge creates a new commit in the feature branch that combines the histories of both branches, preserving the original state of each branch. While this approach is simple and safe, it can result in a cluttered history for your feature branches.
Git Rebase
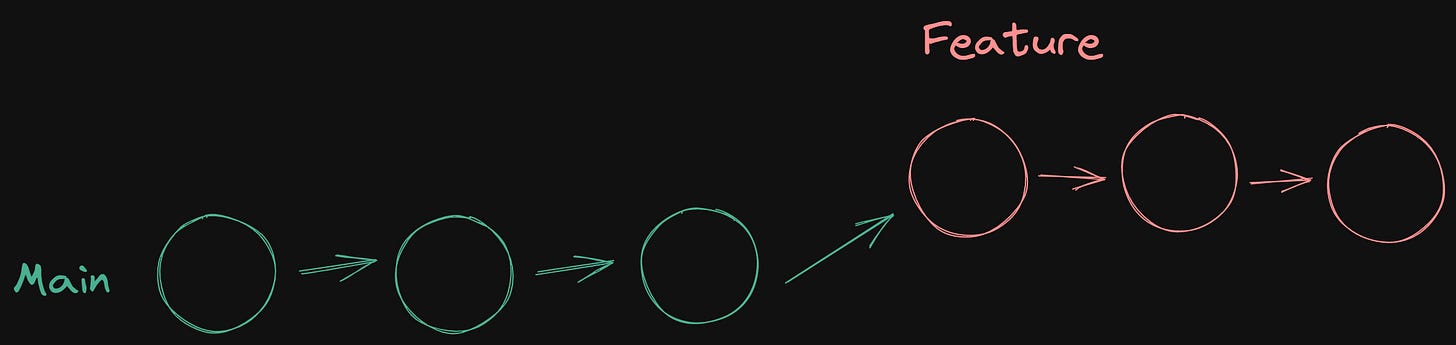
Git rebase offers an alternative approach to integrating changes from one branch into another. Instead of creating a new commit that combines the histories of both branches, rebase modifies the feature branch by replaying its commits on top of the main branch. This effectively moves the entire feature branch to a new base, as if it had been created directly off the latest version of the main branch.
The result is a linear history that appears as if the work on the feature branch was done after the work on the main branch. This can make it easier to understand the sequence of changes and can help keep your project history clean and organized.
Caution: Using Git Rebase
While git rebase has its advantages, its important to note that it rewrites the project history by creating new commits for each commit in the feature branch. This can potentially cause problems, which well discuss in a moment. But first, lets look at some of the benefits of using rebase.
One advantage of rebase is that it eliminates the need for the extra merge commits that are required when using git merge. This results in a linear project timeline, with a single, easy-to-follow line of development instead of the tangled metro lines that can result from merging.
Avoiding a disaster
Tinkering with time is a dangerous act. Now that you know about rebasing, the most important thing to learn is when to avoid it.
Never rebase a branch used by other people.
One key rule to follow is to never rebase a branch that is being used by other people. For example, imagine what would happen if you were to rebase the dev branch onto the main branch. The rebase would move all of the commits in dev in front of main, but this change would only be reflected in your local repository. Other developers would still be working with the original dev branch.
Since rebase creates new commits, git would see your dev branch history as having diverged from everyone elses. This can cause confusion and conflicts. For shared branches, its best to stick with using merge.
Tips on fixing rebase mistakes
If you make a mistake while using git rebase, there are a few ways to fix it. One way is to use the git reflog command to find the reference to the state of your branch before the rebase, and then use git reset to restore your branch to that state.
For example, if you accidentally rebased the dev branch onto the main branch and want to undo the rebase, you can do the following:
Run
git reflogand find the reference to the state of thedevbranch before the rebase. It will look something likedev@{1}.Run
git reset --hard dev@{1}to reset thedevbranch to its state before the rebase.
Its important to note that this will discard any changes made during or after the rebase, so make sure you really want to undo the rebase before proceeding.
Another way to fix a mistake made during a rebase is to use the --abort option with the git rebase command. This will abort the rebase and return your branch to its state before the rebase began. For example, if youre in the middle of a rebase and realize you made a mistake, you can run git rebase --abort to cancel the rebase and start over.

